Strategic talent management: understanding the 9-Box Grid model to identify potential and unlock performance
A deep dive into the 9-Box Grid model for business leaders
In the ever-evolving landscape of business leadership, the effective management of talent has become a cornerstone for organisational success. Among the myriad tools available, the 9-Box Grid model stands out as a nuanced approach to optimising employee performance, potential and strategising accordingly. In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the intricacies of this model, especially as it expands into nine boxes, and how it can serve as a catalyst for succession planning, employee engagement, and reward and recognition strategies.
Understanding the 9-Box Grid model
The 9-Box Grid model is a sophisticated matrix that classifies employees based on two crucial dimensions: performance and potential. In this expanded version, nine boxes emerge, each offering a distinct perspective on an employee’s current contributions and future growth possibilities.
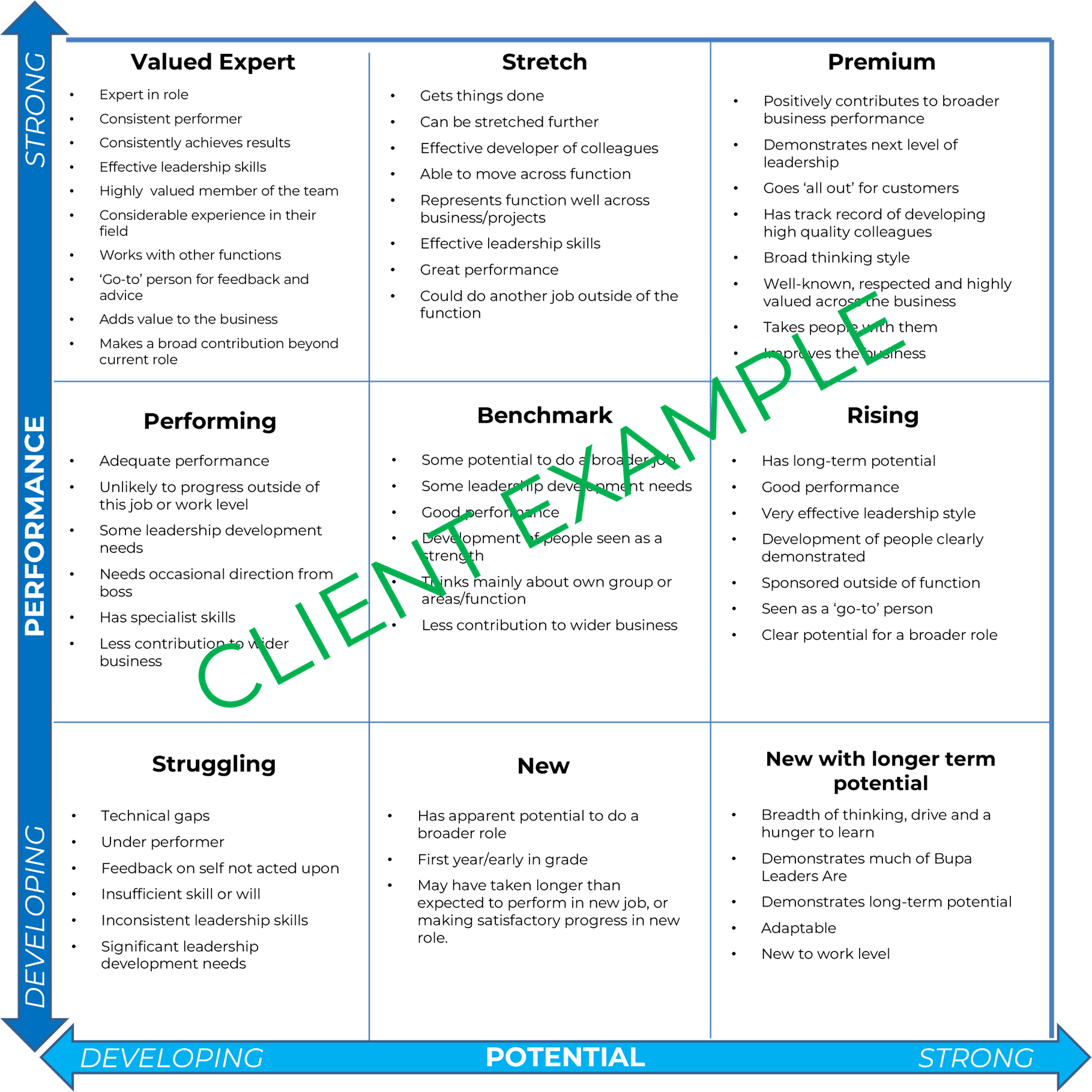
1. High performers with high potential (top right):
This quadrant spotlights individuals excelling in their current roles while demonstrating high potential for future leadership positions. Crucial for succession planning, these high performers necessitate targeted resources for leadership programmes and mentorship to foster their growth.
2. High performers with limited potential (top middle):
Occupied by employees excelling in their current roles but with limited potential for vertical growth. This quadrant prompts business leaders to keep them engaged through specialised projects or lateral moves, maintaining their enthusiasm and contribution.
3. High performance with limited potential (top left):
In this quadrant, individuals with a high level of performance are identified. Strategic interventions such as targeted training and mentorship, become essential to bridge the potential gap and unlock their capabilities.
4. Individuals who are performing demonstrating potential (middle right):
Reserved for individuals with untapped potential. This quadrant concentrates on integrating them into the organisation. Effective onboarding, training, and mentorship programmes are crucial to nurture their potential and ensure a seamless integration.
5. Balanced performers with balanced potential (middle middle):
Employees demonstrating a balance between current performance and future potential fall into this stable quadrant. This group may benefit from ongoing development opportunities to ensure sustained contributions and maintain equilibrium.
6. Low potential with limited performance (middle left):
Individuals with limited potential and struggling in current roles occupy this quadrant. Clear communication, support, and potential role realignment are necessary to address their performance issues and guide them towards improvement.
7. Low performers with high potential (bottom right):
Identifying individuals with current, unproven performance but showing potential for growth. This quadrant emphasises tailored training and mentorship programmes. By unlocking their potential, business leaders can elevate their contributions and harness latent talents.
8. Low performers with balanced potential (bottom middle):
This quadrant includes employees with low current performance but balanced potential. Targeted interventions, support, and a strategic approach to development can help improve their contributions and guide them towards a more balanced state.
9. Low performers with limited potential (bottom left):
The final quadrant encompasses individuals struggling in both performance and potential. A delicate approach is required, with options ranging from performance improvement plans to exploring alternative roles within the organisation.
Implementation for business leaders
Implementing the 9-Box Grid model with its nine performance-based boxes demands a strategic and data-driven approach:
1. Data-driven decisions: Found decisions on comprehensive performance metrics, feedback, and potential assessments. Utilise data analytics tools for deeper insights, providing a solid foundation for informed decision-making.
2. Strategic placement: Regularly map employees on the 9-Box Grid, identifying their current status and future potential. This ongoing process ensures a dynamic understanding of the talent landscape within the organisation.
3. Tailored growth strategies: Craft individualised development plans for each quadrant. Focus on leadership development for top-right performers, specialised projects for top-middle, targeted training and mentorship for top-left, effective onboarding for middle-right, ongoing development for middle-middle, support and realignment for middle-left, tailored training and mentorship for bottom-right, targeted interventions for bottom-middle, and a careful approach for bottom-left.
4. Continuous evaluation: Regularly review and update the 9-Box Grid to adapt to evolving business needs. As the organisation grows and changes, so will the talent landscape, necessitating continuous evaluation and adjustment.
Succession planning
Succession planning is inherently woven into the fabric of the 9-Box Grid model, particularly in the top-right quadrant. Identifying high performers with high potential allows business leaders to mentor and strategically position them for future leadership roles. Investment in leadership programmes and mentorship ensures a robust succession pipeline.
Employee engagement
The 9-Box Grid model offers a unique perspective on employee engagement across various quadrants. For high performers in the top-middle quadrant, engagement can be sustained through specialised projects, ensuring they remain motivated and committed. In the balanced performers with balanced potential (middle-middle) quadrant, maintaining ongoing development opportunities is essential for sustaining a positive and engaged workforce.
Reward and recognition strategies
Reward and recognition strategies are inherently tied to the specific needs of each box. For high performers with high potential (top-right), formal recognition and leadership opportunities are paramount. In contrast, low performers with high potential (bottom-right) may respond well to recognition tied to improved development, creating a positive feedback loop.
Having the right salary levels in place, which are market competitive, is a guaranteed way to ensure you retain and motivate current talent, as well as having that edge to attract new talent.
The best way to be keep on top of the market trends and know what your competitors are doing is to regularly benchmark your roles – and not all your salaries need to be above the market median to be competitive!
Conclusion
Strategic talent management is the linchpin for sustained organisational success. The 9-Box Grid model, with its nine performance-based boxes, serves as a compass for business leaders, guiding them through the intricate journey of employee performance and potential. By leveraging this model and integrating it seamlessly into succession planning, employee engagement, and reward and recognition strategies, leaders can create a roadmap for long-term success. As organisations evolve, so too must their talent management strategies, and the 9-Box Grid model provides a flexible framework to adapt and thrive in the ever-changing business environment. Contact us today to unlock the full potential of your talent.
Further information
For a deeper understanding of how the 9-Box Grid model can transform your talent management strategy and drive organisational success, contact us. Our team of HR and reward specialists are ready to provide personalised insights and guide you through the implementation process.
Ready to reshape your organisation for lasting success?
Contact us 02044582 1779 or peopleadvisory@mks.co.uk.

